Climate - truthful information about climate, related activism and politics.
6443 readers
445 users here now
Discussion of climate, how it is changing, activism around that, the politics, and the energy systems change we need in order to stabilize things.
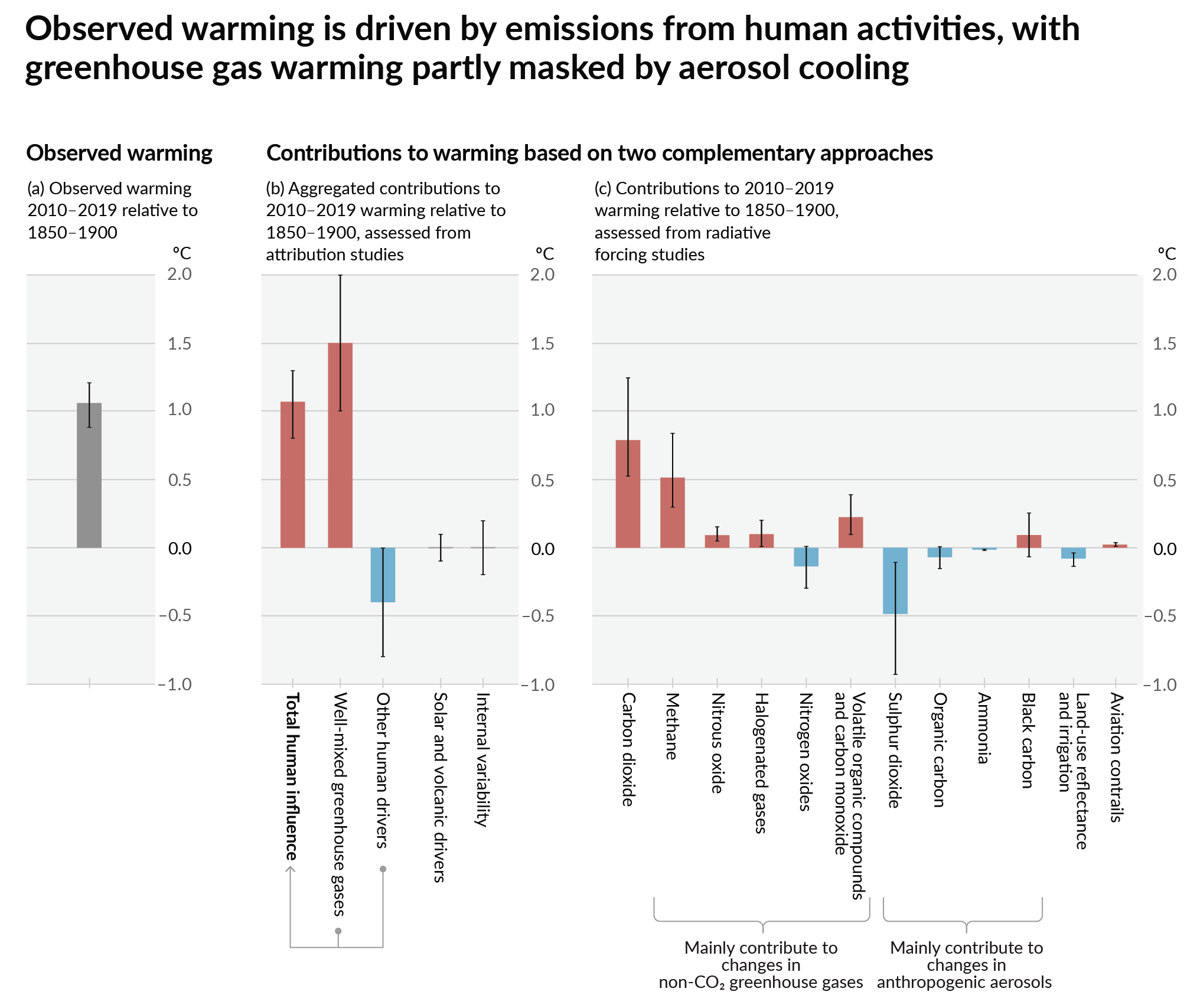
As a starting point, the burning of fossil fuels, and to a lesser extent deforestation and release of methane are responsible for the warming in recent decades:

How much each change to the atmosphere has warmed the world:
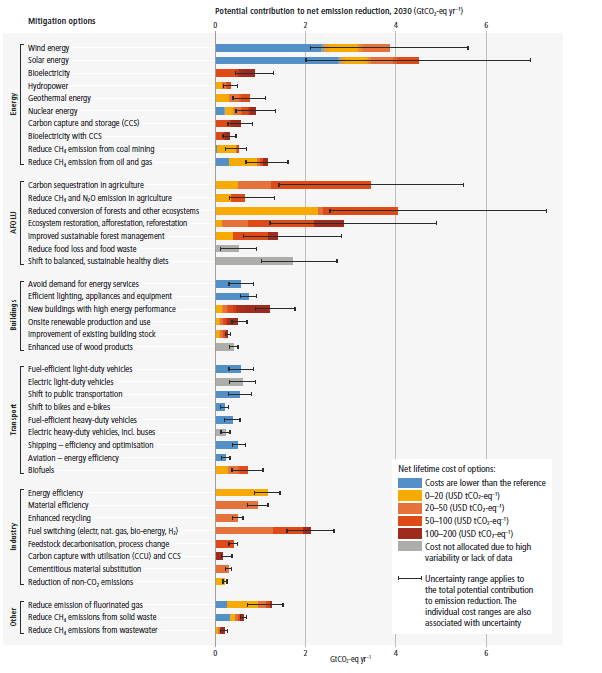
Recommended actions to cut greenhouse gas emissions in the near future:
Anti-science, inactivism, and unsupported conspiracy theories are not ok here.
founded 2 years ago
MODERATORS
51
52
76
Paris said au revoir to cars. Air pollution maps reveal a dramatic change.
(www.washingtonpost.com)
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
29
Australia’s biggest industrial polluter receives millions in carbon credits despite rising emissions
(www.theguardian.com)
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75


